What is glaucoma?
Additional Pages
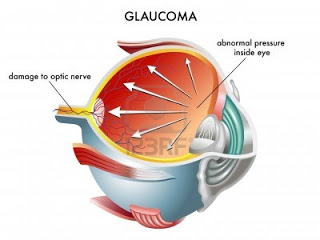
Glaucoma is a characteristic loss of the field of vision most often associated with the build-up of pressure inside your eye. Aqueous fluid, which fills the space at the front of the eye just behind the cornea (the clear lens covering the front of the eye), is produced behind the iris (the coloured part of the eye) in the ciliary body. It flows through the pupil (the dark hole in the centre of the iris), and drains from the anterior chamber angle, which is the junction between the edge of the iris and the cornea. This fluid provides oxygen and nutrients to the clear structures at the front of the eye.
If this outflow of liquid is impaired at all, there is a build-up of pressure inside the eye that damages the optic nerve, which carries visual images to the brain. The result is a loss of peripheral vision.
Thus, while glaucoma sufferers may be able to read the smallest line on the vision test, they may find it difficult to move around without bumping into things or to see moving objects to the side, such as cars.
The best defense against glaucoma is regular eye examinations. Glaucoma most often strikes people over age 40, but it is recommended that during adult life everyone be tested at least every two years. Some people with glaucoma do experience symptoms, but symptoms vary depending on the type of glaucoma.
Types of glaucoma
By far the most common type, primary open-angle glaucoma develops gradually and painlessly. Since there are no early warning signs, it can slowly destroy your vision without you knowing it. The first indication may only occur after some considerable vision loss.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma results from a sudden blockage of the drainage channels in your eye accompanied by blurred vision, the appearance of coloured rings in the eyes, and sometimes extreme pain or redness in the eyes.
What causes glaucoma?
Some causes are known, others are not. Causes differ depending on the type of glaucoma. The exact cause of open-angle glaucoma, where the drainage channels for the aqueous appear to be open and clear, is not known.
Closed-angle glaucoma can occur when the pupil dilates or gets bigger and bunches the iris up around its edge, blocking the drainage channel. An injury, infection or tumor in or around the eye can also cause internal eye pressure to rise either by blocking drainage or displacing tissues and liquid within the eye. A mature cataract also can push the iris forward to block the drainage angle, between the iris and the cornea.
Glaucoma can occur secondarily to a number of other conditions, such as diabetes, or as a result of some medications for other conditions
Who gets glaucoma?
Glaucoma most frequently occurs after age 40, but can occur at any age. If you’re of African heritage, you are more likely to develop open-angle glaucoma – and at an earlier age – than if you’re Caucasian. Asians are more likely to develop closed-angle glaucoma. You have a higher risk of developing glaucoma if a close family member has it or you have high blood pressure or high blood sugar (diabetes). There is also a greater tendency for glaucoma to develop in individuals who are nearsighted. Those at heightened risk for glaucoma should have their eyes checked at least once a year.
Why is glaucoma harmful to vision?
The optic nerve, located at the back of the eye, carries visual information to the brain. As the fibers that make up the optic nerve are damaged by glaucoma, the amount and quality of information sent to the brain decreases and a loss of field of vision occurs.
Will I go blind from glaucoma?
If diagnosed at an early stage, glaucoma can be controlled and little or no further vision loss should occur. If left untreated, side awareness (peripheral vision) will be destroyed and blindness may occur. Ultimately, even central vision may be lost.
How is glaucoma detected?
Tests for glaucoma are part of a comprehensive eye examination. A simple and painless procedure called tonometry measures the internal pressure of your eye. Ophthalmoscopy examines the back of the eye to observe the health of the optic nerve. Your eye care practitioner may also do a visual field test, a very sensitive test that checks for the development of abnormal blind spots.
How is glaucoma treated?
Glaucoma is usually treated with prescription eye drops and medicines. In some cases, surgery may be required to improve drainage. The goal of the treatment is to prevent loss of field of vision by lowering the pressure in the eye. The treatment to lower the pressure must normally be continued for a long period of time.
There are many products available to treat glaucoma and your doctor will select a product most appropriate for you.
Will my vision be restored after treatment?
Unfortunately, any vision loss as a result of glaucoma is permanent and cannot be restored. This is why regular eye examinations are important.
Can glaucoma be prevented?
No, but early detection and treatment can control glaucoma and reduce the chances of damage to the eye and a loss of sight.

You must be logged in to post a comment.